Drug Interaction: What You Need to Know About Medication Risks and Safe Combos
When you take more than one medication, or even a medicine with certain foods or supplements, you might be risking a drug interaction, a reaction between two or more substances that changes how one or both work in your body. Also known as medication interaction, it’s not just about pills clashing—it’s about your body’s chemistry getting thrown off in ways you can’t always feel until it’s too late. This isn’t rare. One in four adults takes five or more medications, and each added drug increases the chance of something going wrong. A simple combo like linezolid, an antibiotic used for tough infections with aged cheese or red wine can spike your blood pressure to dangerous levels. Or taking digoxin, a heart medication that helps control rhythm with certain antibiotics can build up toxic levels in your blood. These aren’t hypotheticals—they’re real, documented cases that land people in the ER.
Drug interactions don’t always come from other pills. They can hide in your grocery cart. tyramine-rich foods, like cured meats, fermented cheeses, and draft beer can turn a routine antibiotic into a life-threatening event. Even something as common as grapefruit juice can wreck how your liver processes cholesterol meds, blood pressure drugs, or even some anxiety pills. And it’s not just what you eat—supplements like St. John’s wort can make birth control, antidepressants, or HIV meds useless. Your pharmacist doesn’t just fill prescriptions; they’re your first line of defense against these hidden traps.
Some interactions are obvious if you know what to look for. A sudden headache, dizziness, nausea, or unexplained fatigue after starting a new drug? That’s your body signaling something’s off. Other times, the effect is silent—your blood sugar drops, your heart rate changes, or your kidneys struggle to clear the mix. That’s why knowing your meds matters. Don’t assume your doctor knows every pill you take. Keep a list: prescription, over-the-counter, vitamins, herbs. Bring it to every appointment. Ask: "Could this interact with anything else I’m taking?" And never ignore a warning label. If it says "avoid grapefruit," it’s not a suggestion—it’s a safety rule.
The posts below cover real-world cases where drug interactions changed lives. You’ll find out why you must wait 14 days after stopping linezolid before eating certain cheeses, how digoxin levels can spike with common antibiotics, and why mixing alcohol with AUD meds can undo months of progress. We break down what happens in your body when drugs collide, what to avoid, and how to spot trouble before it hits. Whether you’re managing heart disease, diabetes, mental health, or just taking a few pills daily, this collection gives you the facts you need to stay safe—no jargon, no fluff, just what works.
Levodopa and Antipsychotics: How Opposing Dopamine Effects Worsen Symptoms
Levodopa and antipsychotics have opposing effects on dopamine, making it dangerous to use them together. This article explains how this interaction worsens symptoms in Parkinson’s and schizophrenia patients, and what new treatments are emerging.
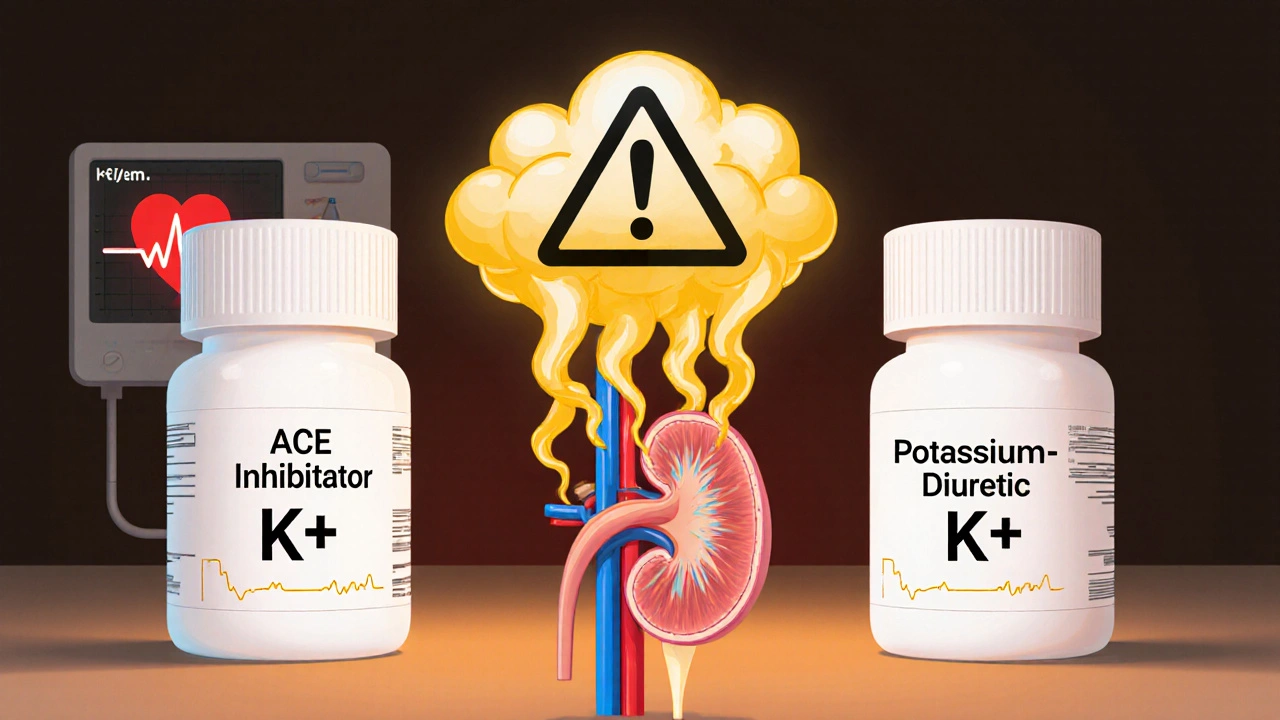
Read moreACE Inhibitors and Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: Understanding the Hyperkalemia Risk
Combining ACE inhibitors and potassium-sparing diuretics can raise potassium to dangerous levels, increasing the risk of heart rhythm problems. Learn how to monitor, manage, and reduce this common but preventable drug interaction.
Read more