Category: Medications - Page 2
Authorized Generics vs Brand Drugs: What You Need to Know About Identical Medications
Authorized generics are the exact same drugs as brand-name medications, made by the same company with identical ingredients. Learn how they differ from regular generics, why they cost less, and when to ask for them at the pharmacy.
Read moreWhat Each Part of Your Rx Medication Label Means for Patients
Understand every part of your prescription label-from your name to the expiration date-to avoid dangerous mistakes. Learn what each section means and how to use it for safer medication use.
Read moreGeneric Patent Case Law: Landmark Court Decisions That Shape Drug Access
Landmark court decisions in generic patent law shape whether affordable drugs reach patients. Key rulings like Amgen v. Sanofi and Allergan v. Teva are redefining how patents are challenged and enforced in the pharmaceutical industry.
Read moreHow to Store Insulin and Biologics During Long Flights: A Practical Guide
Learn how to safely store insulin and biologics during long flights with proven methods, temperature guidelines, and airline tips to avoid dangerous medication damage while traveling.
Read moreHow to Use Compounded Medications for Children Safely
Compounded medications for children can be lifesaving-but only if used safely. Learn how to verify dosing, choose accredited pharmacies, and avoid deadly errors with custom-formulated drugs.
Read moreAcarbose and Miglitol: How to Manage Flatulence and GI Side Effects
Learn how to manage gas, bloating, and GI side effects from acarbose and miglitol with proven dose titration, dietary tips, and OTC solutions that actually work-without quitting the medication.
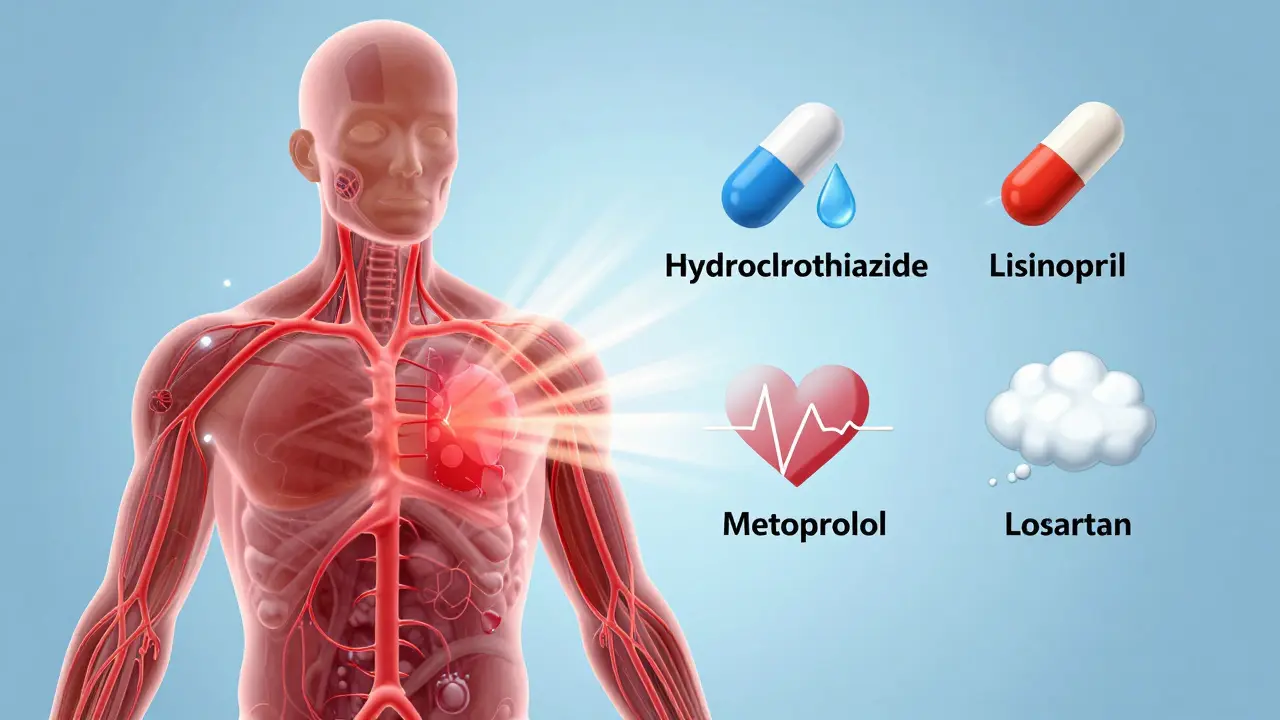
Read moreBlood Pressure Medications: Types, Side Effects, and Safety
Learn the most common blood pressure medications, their side effects, and safety tips. Understand why certain drugs are chosen based on your health and how to avoid dangerous interactions.
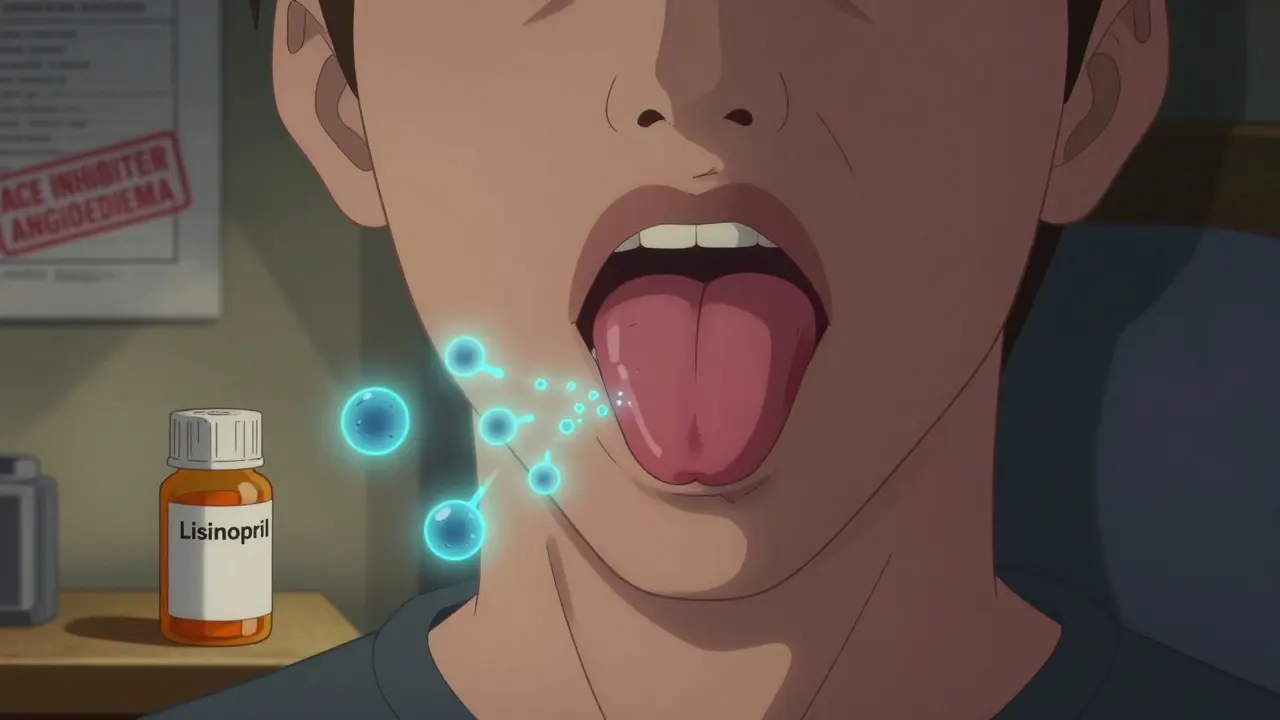
Read moreACE Inhibitor Angioedema: How to Recognize Swelling as a Drug Reaction
ACE inhibitor angioedema is a dangerous, often misdiagnosed drug reaction causing sudden facial or throat swelling. Unlike allergies, it doesn't respond to epinephrine or antihistamines. Learn how to recognize it, what actually works, and why stopping the drug is the only cure.
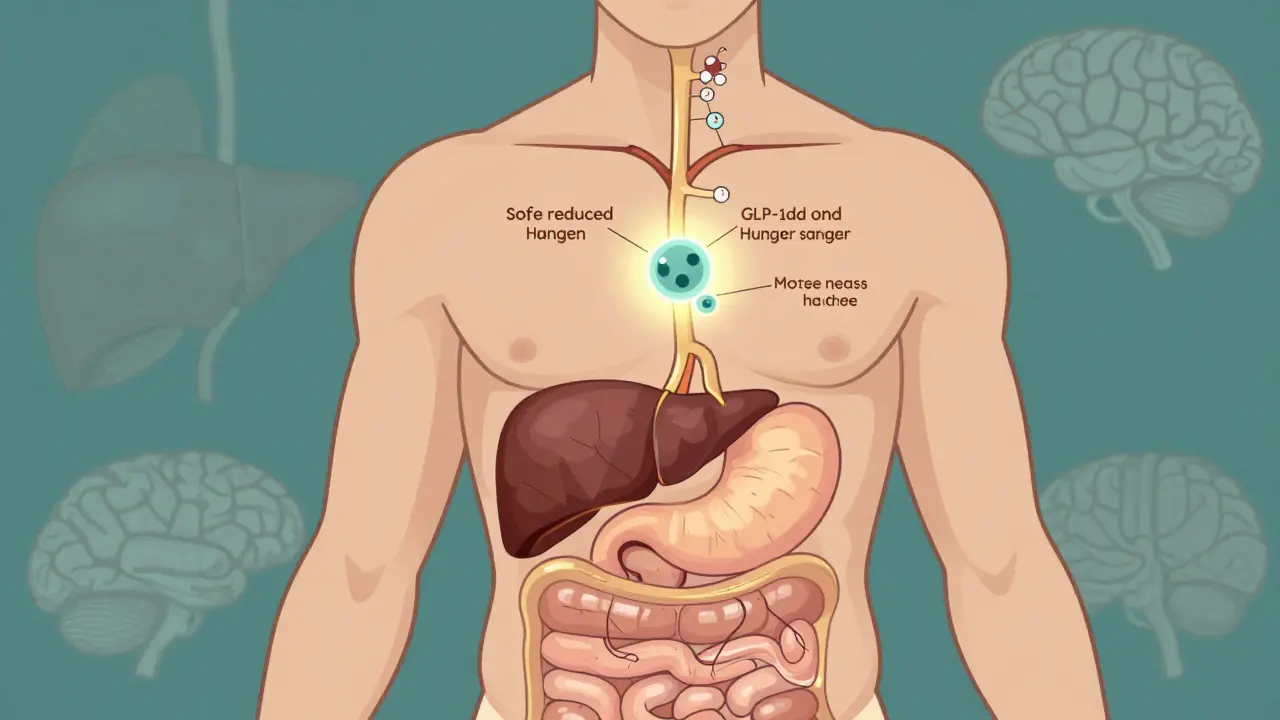
Read moreGLP-1 Agonists and Weight Loss: How These Diabetes Drugs Are Changing Obesity Treatment
GLP-1 agonists like Ozempic and Wegovy were designed for diabetes but now lead the weight loss revolution. Learn how they work, who benefits most, their surprising brain and heart perks, and the real costs and side effects.
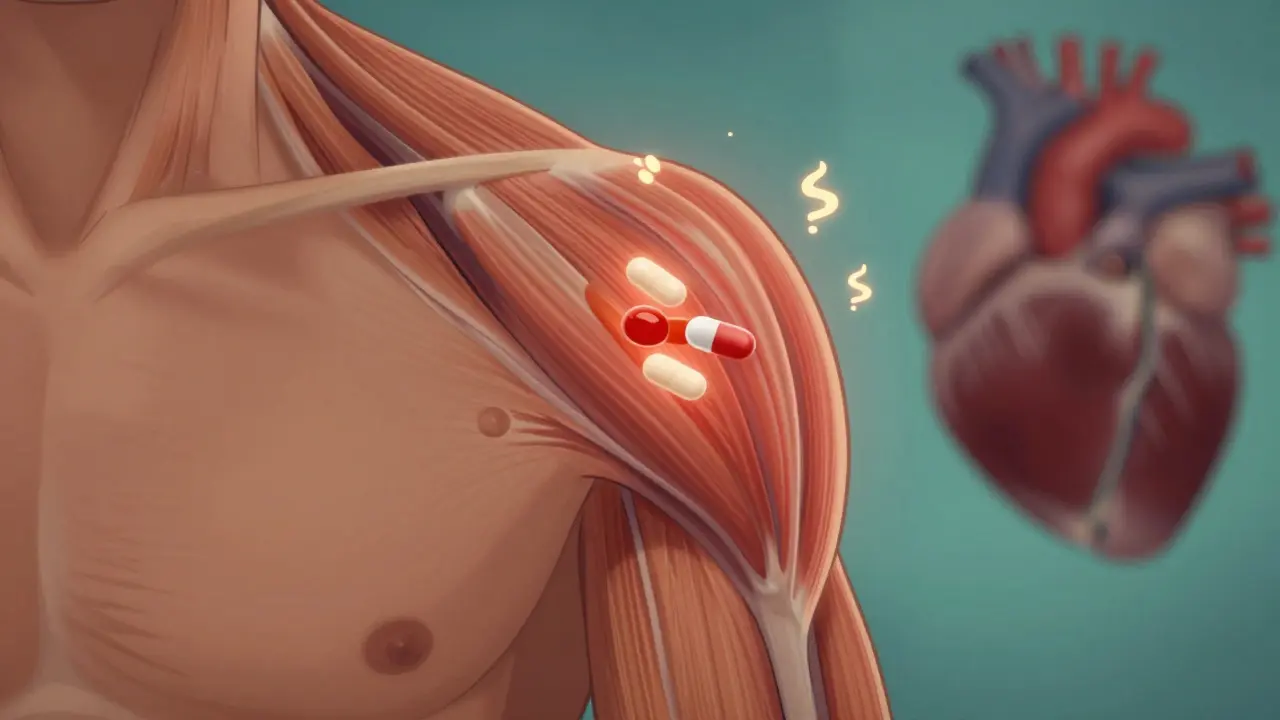
Read moreStatin-Induced Muscle Pain: Understanding Myalgia and Myositis
Statin-induced muscle pain affects up to 30% of users, ranging from mild myalgia to severe immune-mediated myositis. Learn the differences, warning signs, and what to do if you're experiencing muscle weakness or pain while on statins.
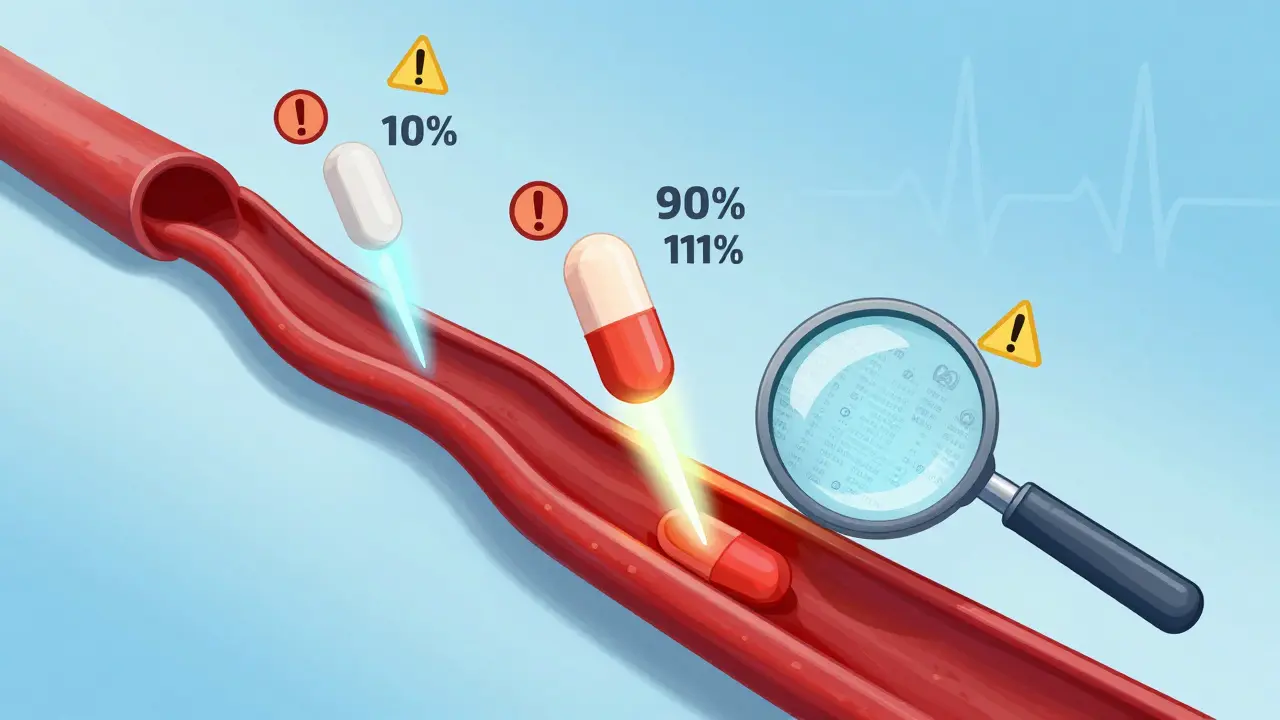
Read moreFDA Bioequivalence Standards for NTI Drugs: Special Requirements Explained
The FDA applies strict bioequivalence rules to narrow therapeutic index (NTI) drugs like warfarin and phenytoin, requiring tighter limits (90-111%) and lower variability than standard generics to ensure safety and efficacy.
Read moreOral Corticosteroid Burden in Severe Asthma: Proven Alternatives That Work
Oral corticosteroids help control severe asthma but come with dangerous long-term side effects. Learn about proven alternatives like biologics that reduce steroid dependence, lower hospitalizations, and improve quality of life.
Read more